A parent-friendly explanation of how the FEIE Standard Deduction impacts family tax filing
All You Required to Find Out About the Foreign Earned Income Exclusion and Its Link to the Common Deduction
The Foreign Earned Earnings Exemption (FEIE) offers a vital possibility for U.S. residents and resident aliens working abroad to decrease their gross income. Recognizing the qualification requirements and asserting process is crucial. The communication between the FEIE and the conventional deduction can make complex tax approach. Errors in steering these regulations can cause missed advantages. Exploring these facets exposes crucial info for reliable tax obligation planning and maximizing economic advantages.
Recognizing the Foreign Earned Earnings Exemption (FEIE)
The International Earned Income Exclusion (FEIE) works as an essential tax obligation stipulation for U.S. people and resident aliens who function abroad, permitting them to omit a significant part of their foreign-earned income from U.S. government taxes. This stipulation is vital for individuals living outside the United States, as it aids reduce the economic burden of double taxation on income earned in foreign nations. By using the FEIE, qualified taxpayers can reduce their gross income considerably, advertising economic security while living and working overseas. The exclusion amount is changed each year for inflation, guaranteeing it shows existing financial problems. The FEIE is especially advantageous for those in areas with a higher price of living, as it permits them to retain more of their profits. Understanding the mechanics and effects of the FEIE empowers expatriates to make informed economic choices and maximize their tax scenarios while living abroad.
Qualification Demands for the FEIE
To receive the Foreign Earned Income Exclusion, people should meet particular eligibility demands that include the Residency Examination and the Physical Visibility Examination. Furthermore, work standing plays an important role in figuring out eligibility for this tax advantage. Understanding these criteria is important for anybody seeking to capitalize on the FEIE.
Residency Test Standard
Figuring out qualification for the Foreign Earned Revenue Exclusion (FEIE) depends upon conference specific residency test standards. Primarily, individuals should develop their tax obligation home in an international country and demonstrate residency via either the bona fide home test or the physical visibility test. The bona fide home test calls for that a taxpayer has actually established an irreversible residence in a foreign country for an uninterrupted duration that covers an entire tax year. This entails demonstrating intent to make the foreign location a primary home. In addition, the taxpayer has to exhibit connections to the foreign country, such as protecting real estate, family, or employment links. Fulfilling these residency requirements is vital for receiving the FEIE and properly lowering tax obligation obligations on made earnings abroad.
Physical Existence Examination
Satisfying the residency requirements can also be achieved via the physical visibility examination, which uses an alternate path for getting the Foreign Earned Income Exemption (FEIE) To please this test, a specific need to be physically existing in an international nation for at the very least 330 full days during a consecutive 12-month duration. This need stresses the importance of real physical existence, instead of simply keeping a residence abroad. The 330 days do not need to be successive, enabling flexibility in traveling arrangements. This examination is especially valuable for united state citizens or locals working overseas, as it allows them to omit a significant section of their foreign gained earnings from U. FEIE Standard Deduction.S. tax, thus decreasing their total tax responsibility
Employment Standing Needs
Eligibility for the Foreign Earned Revenue Exemption (FEIE) depends upon specific employment condition requirements that people must fulfill. To qualify, taxpayers have to demonstrate that their revenue is originated from international sources, usually with employment or self-employment. They need to be either an U.S. citizen or a resident alien and keep a tax obligation home in an international country. Additionally, individuals must fulfill either the Physical Existence Examination or the Authentic House Examination to establish their foreign standing. Independent individuals must report their web earnings, ensuring they do not go beyond the recognized exemption restrictions. It's essential for applicants to keep correct paperwork to confirm their claims relating to employment condition and foreign earnings throughout the tax obligation year.
Just how to Assert the FEIE
Eligibility Requirements Clarified
For people seeking to profit from the Foreign Earned Income Exemption (FEIE), understanding the eligibility requirements is important. To qualify, one need to meet two key tests: the authentic house test or the physical presence test. The authentic residence test puts on those that have developed an irreversible house in a foreign nation for an undisturbed period, commonly a year or more. On the other hand, the physical presence examination needs individuals to be physically present in an international country for at least 330 days during a 12-month period. FEIE Standard Deduction. Furthermore, just gained income from international sources gets exclusion. Fulfilling these criteria is crucial for taxpayers wanting to minimize their taxed earnings while living abroad
Essential Tax Return
How can one successfully assert the Foreign Earned Income Exemption (FEIE)? To do so, certain tax obligation types must be utilized. The primary form needed is internal revenue service Type 2555, which allows taxpayers to report foreign earned revenue and claim the exemption. This type requires detailed information about the individual's foreign residency and the earnings made while living abroad. Furthermore, if declaring the exemption for real estate expenses, Type 2555-EZ may be utilized for simplicity, supplied specific requirements are satisfied. It is crucial to ensure that all required sections of click here to find out more the forms are finished properly to prevent hold-ups or problems with the IRS. Understanding these kinds is crucial for optimizing the advantages of the FEIE.
Filing Process Steps
Declaring the Foreign Earned Earnings Exclusion (FEIE) entails a collection of clear and organized actions. First, people need to determine their qualification, verifying they fulfill the physical presence or bona fide house examinations. Next, they must complete internal revenue service Type 2555, detailing revenue earned abroad and any relevant exclusions. It is necessary to collect sustaining documents, such as foreign tax obligation returns and evidence of residence (FEIE Standard Deduction). After completing the type, taxpayers need to attach it to their annual income tax return, typically Type 1040. Filing online can improve this procedure, but making certain precise details is important. Finally, individuals need to maintain duplicates of all submitted forms browse this site and sustaining papers for future reference in situation of audits or queries from the internal revenue service
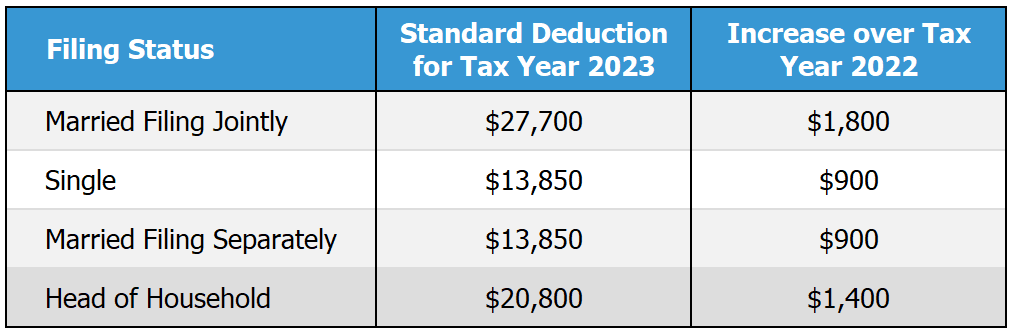
The Standard Deduction: An Introduction
The standard deduction works as a crucial tax obligation benefit that streamlines the declaring procedure for several individuals and households. This deduction permits taxpayers to reduce their taxable income without the need to make a list of reductions, making it an attractive option for those with simple economic scenarios. For the tax obligation year, the standard deduction amount varies based on filing status, with different thresholds for single filers, wedded pairs submitting collectively, and heads of household.
The basic deduction is changed yearly for inflation, ensuring its significance gradually. Taxpayers who qualify can choose between the standard reduction and detailing their deductions, generally opting for the better benefit. By supplying a standard deduction, the common deduction supports taxpayers in reducing their overall tax obligation liability, thus enhancing their economic setting. Understanding the conventional deduction is crucial for reliable tax planning and taking full advantage of prospective savings for families and people alike.
Interaction Between FEIE and Standard Reduction
While both the Foreign Earned Income Exemption (FEIE) and the standard reduction serve to reduce taxable revenue, their communication can considerably impact a taxpayer's total tax liability. Taxpayers who get approved for the FEIE can omit a significant amount of their foreign-earned revenue, which might affect their qualification for the standard deduction. Particularly, if a taxpayer's international earnings is completely omitted under the FEIE, their gross income might fall listed below the limit necessary to assert the conventional reduction.
It is crucial to note that taxpayers can not double-dip; they can not utilize the very same earnings to claim both the FEIE and the standard deduction. This suggests that mindful consideration is needed when figuring out the ideal approach for tax obligation decrease. Eventually, recognizing exactly how these 2 arrangements engage makes it possible for taxpayers to make informed decisions, guaranteeing they optimize their tax advantages while remaining certified with IRS policies.
Tax Obligation Benefits of Using the FEIE
Utilizing the Foreign Earned Income Exclusion (FEIE) can provide notable tax obligation benefits for united state residents and resident aliens living and working abroad. This exclusion permits qualified people to exclude a specific quantity of foreign-earned earnings from their gross income, which can lead to substantial tax savings. For the tax obligation year 2023, the exclusion amount is up to $120,000, considerably decreasing the taxable revenue reported to the internal revenue service.

Furthermore, the FEIE can assist avoid double tax, as foreign taxes paid on this revenue might additionally be eligible for credit scores or reductions. By purposefully utilizing the FEIE, taxpayers can maintain more of their earnings, permitting enhanced financial security. The FEIE can be useful for those who qualify for the bona fide home test or physical existence examination, supplying versatility in managing their tax responsibilities while living overseas. On the whole, the FEIE is an important device for migrants to maximize their funds.

Common Errors to Avoid With FEIE and Typical Reduction
What pitfalls should taxpayers understand when claiming have a peek at these guys the Foreign Earned Earnings Exemption (FEIE) along with the standard deduction? One typical mistake is presuming that both benefits can be claimed concurrently. Taxpayers should comprehend that the FEIE must be asserted prior to the standard deduction, as the exclusion essentially reduces taxable income. Failing to meet the residency or physical presence examinations can also bring about ineligibility for the FEIE, leading to unanticipated tax obligations.
Additionally, some taxpayers neglect the requirement of appropriate documents, such as preserving documents of international earnings and traveling dates. Another constant error is miscalculating the exemption amount, possibly due to inaccurate forms or misinterpretation of tax obligation policies. Inevitably, individuals must bear in mind that declaring the FEIE can affect eligibility for sure tax credit ratings, which can complicate their general tax circumstance. Awareness of these mistakes can assist taxpayers navigate the complexities of global taxation a lot more properly.
Often Asked Questions
Can I Assert FEIE if I Live Abroad Part-Time?
Yes, an individual can declare the Foreign Earned Earnings Exemption if they live abroad part-time, given they meet the essential requirements, such as the physical visibility or authentic residence tests outlined by the IRS.
Does FEIE Influence My State Tax Obligation Commitments?
The Foreign Earned Income Exclusion (FEIE) does not straight affect state tax commitments. States have differing guidelines concerning revenue earned abroad, so people should consult their details state tax obligation policies for precise assistance.
Exist Any Kind Of Expiry Dates for FEIE Claims?
Foreign Earned Income Exclusion (FEIE) insurance claims do not have expiry days; however, they must be declared annually on income tax return. Failing to case in a provided year may lead to lost exemption advantages for that year.
Exactly How Does FEIE Influence My Social Protection Conveniences?
The Foreign Earned Revenue Exemption (FEIE) does not straight impact Social Protection benefits, as these advantages are based upon lifetime revenues. Omitted income might minimize general revenues, potentially influencing future advantage calculations.
Can I Revoke My FEIE Insurance Claim After Filing?
Yes, a person can withdraw their International Earned Earnings Exclusion case after filing. This abrogation has to be submitted via the suitable tax obligation kinds, and it will affect their tax obligation obligations and prospective deductions moving ahead.
The Foreign Earned Income Exemption (FEIE) presents an essential opportunity for United state residents and resident aliens working abroad to decrease their taxable earnings. Recognizing the Foreign Earned Income Exclusion (FEIE)
The Foreign Earned International Exclusion RevenueExemption) serves as an essential tax provision tax obligation Arrangement citizens and residents aliens who work abroadFunction allowing them to exclude a leave out portion substantial part foreign-earned income from Earnings federal taxationGovernment While both the Foreign Earned Revenue Exemption (FEIE) and the standard deduction offer to minimize taxable income, their communication can greatly influence a taxpayer's overall tax liability. Using the Foreign Earned Earnings Exemption (FEIE) can supply remarkable tax obligation benefits for United state people and resident aliens living and working abroad. Foreign Earned Income Exclusion (FEIE) claims do not have expiry days; however, they should be declared every year on tax obligation returns.